Y
Ecology @ 10:36 PM
11) Why is there a need for conservation?
Conservation is necessary for the maintenance of the Earth's biodiversity. It is to prevent extinction of plant and animal species.Conservation is needed to:-To maintain a balanced ecosystem-To maintain a large gene pool-To maintain biodiversity-To ensure the conservation of marine life-Conservation for scientific studies-Conservations preserve natural scenery and wildlife
Y
Ecology @ 5:43 AM
10) Discuss the impact of human activities on our ecosystem, highlighting issues on deforestation, over-fishing, eutrophication, biomagnification.
1)
Deforestation-Soil erosion
Deforestation is the clearing of forests. When the trees are removed, soil is exposed dierctly to the force of the rain. Topsoil, the most fertile layer of soil, gets washed away or eroded during heavy rain, espically when rain falls on steep slopes.
-Flooding
Eroded soil may be deposited in rivers and streams, blocking the flow of water, thus causing floods.-Desertification
Sunlight falls directly onto the soil. Water evaporates rapidly from the soil, which then hardens With the topsoil eroded, the land becomes barren. Plants cannot grow in the soil, Thus, organisms which depend directly or indirectly on plants for food will die off. This is known as desertification.-Climate changes
Rain water that is retained and absorbed by roots of trees is lost as water vapour during transpiration. The water vapour eventually condenses and falls as rain. When trees are cleared, the area becomes dry and warm thus, the annual rainfall decreases.2)
Over-fishingAs human populations increase, so does the demand for fish, thus over fishing i common. If the situation is not controlled, some species of fish are caught faster than they can be replaced. Young fish that are caught will not have a chance to reproduce. Hence, fish populations will decrease.3)
EutrophicationNitrates and phosphates present in the fertilizers are useful nutrients for the growth of algae and water plants. The enrichment of nutrients leads to rapid growth and multiplication of algae and water plants. Submerged algae and water plants die due to lack of sunlight. The dead bodies of the algae and water plants are decomposed by bacteria. Bacteria grow and multiply rapidly, using up oxygen in the water. Thus, other organisms and fish die due to a lack of oxygen.4)
BiomagnificationSome insectisides such at DDT are non-biodegradedable. These insectisides may be carried away into rivers, lakes, streams by rainwater when it is raining. Fish or animals may take in the polluted water. THe insectiside is stored in fatty tissue of the organism and will not be excreted. Organisms feeding at higher levels in the food chain will also get poisoned. And thus they will die and the population will decrease.
Y
Ecology @ 5:00 AM
9) Describe the carbon cycle.
Carbon is constantly being removed from and released into the environment, in the form of carbon dioxide. Hence, the carbon dioxode concentration in the environment remains relatively constant.
A diagram of the carbon cycle:
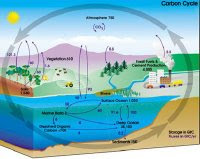
How is carbon dioxide removed from the environment? During photosynthesis, green plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and uses it to manufacture carbohydrates such as glucose. The glucose may be changed to other organic compounds such as fats, amino acids and proteins. The carbon compounds will then become part of the animals' bodies when they consume these green plants. The carbon compounds may also be preserved in fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas, and oil.
How is carbon dioxide released into the environment?
Carbon dioxide is released into the environment through:
-Respiration
-Combustion
-Decomposition
Respiration
When living organisms go through respiration, carbon compounds like glucose are broken down in their bodies and carbon dioxide is released into the environment.
Combustion
When fossil fuels like coal are burnt or undergo combustion, carbon compounds preserved in the fossil fuels are broken down and released into the environment.
Decomposition
When organisms die, their bodies decay or are broken down into simple substances by decomposers. Carbon dioxide is one of the simple substances released into the environment during decay. When the decomposers respire, carbon dioxide is released into the environment.
The carbon cycle is important because:
-It ensures that there is a constant supply of carbon dioxide for plants to carry out
photosynthesis.
-Enables energy to flow through the ecosystem.
Y
Ecology @ 8:37 PM
8) What happens to most of the energy in the ecosystem?
As energy flows through the ecosystem, some of it is lost to the environment at heat. Heat energy cannot be recycled. Hence, energy has to be constantly supplied to the ecosystem. In an ecosystem, energy does not flow in a cycle. Energy is non-cyclic(linear).
Y
Ecology @ 5:28 AM
7) Why are short food chains better?
Short food chains are better as they are more efficient in energy transfer. Since energy is lost at each trophic level, less and less energy is available for the organism at the next level as the food chain goes on. Hence, a shorter food chain means more energy is avaliable for the final consumer because less energy is lost to the environment.
Y
Ecology @ 9:05 PM
6) What are ecological pyramids? Describe the different types of ecological pyramids.
Ecological pyramids can be used to compare trophic levels in a food chain.The three ecological pyramids:
1) Pyramid of numbers
2) Pyramid of biomass
3) Pyramid of energy
1) Pyramid of numbers
The pyramid of numbers allows us to compare the number of organisms present in each tropic level at a present time.

There are also pyramids of numbers which are inverted. It occurs when:
-Organisms on one trophic level are parasitic on organisms on another trophic level.
-Many small organisms of one trophic level feed on a large organism of another trophic level.
2) Pyramid of biomassA pyramid of biomass allows us to compare the mass of organisms present in each trophic level at a particular time.

An ecological pyramid of biomass shows the relationship between biomass and trophic level by quantifying the amount of biomass present at each trophic level at any one time. This is called the standing mass of organisms.
The pyramid of biomass is more accurate than the pyramid of numbers, as the pyramid of numbers may be inverted in some cases while the pyramid of biomass, is based on standard mass. Thus, most of the time it will be broad at the bottom and narrow at the top.
The biomass pyramid may also be 'inverted' which happens when the producer has a very fast rate of reproduction which is fast enough the replace the organisms eaten by the primary consumers.
3) Pyramid of energy
The energy in the various trophic levels of a food chain can be represented in the form of a pyramid. It is known as the pyramid of energy.

The pyramid of energy is constructed based on the total energy level in each trophic level over a certain period of time. A huge amount of energy is lost to the environment as food is transferred from one trophic level to the next. Energy may be lost to the environment in a few ways:
-as heat during respiration at every trophic level
-in uneaten body parts
-through undigested matter egested by consumers
-through waste products excreted by consumers, for example, urea.
Heat energy is wasted as it cannot be recycled in any way in the ecosystem.
Loss of energy occurs as the food chain continues. The total energy at the first trophic level is the highest while the energy at the lowest trophic level is the lowest. Hence, a pyramid of energy is always broad at the bottom and narrow on top. About 90% of the energy is lost during energy transfer from one trophic level to another. The greatest amount of energy lost is during the transfer of energy from producer to primary consumer.
Y
Ecology @ 8:49 PM
5) What is the relationship between predator and prey? Two predators with the same prey?
A predator is an organism that kills and feeds on other organisms. The organisms that are eaten are called the prey.
An increase in the population size of the prey means that more food is available for the predator. Therfore, an increase in population of the predator will be observed. This causes a decrease in the population of the prey, which in turn results in a decreased population of predators as there is less food available. This cycle then repeats itself.
A graph of changes in the population of predators and prey over time:

If there are two predators with the same prey, the population of the predator would be small as there is less food available to both predators. This will cause a jump in the population of the prey as population of both predators are small. The population of the predators would increase as there is more food available, thus causing a decrease in pupulation of prey. This cycle repeats itself.










